
2019 American College of Rheumatology/Arthritis Foundation guideline for the management of osteoarthritis of the hand, hip, and knee. Health benefits of water-based exercise.2021 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Effusion is caused by intrinsic factors, such as internal derangements that. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Undoubtedly, trauma is the most common cause of effusion within the knee joint.
We link primary sources - including studies, scientific references, and statistics - within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations. hemarthrosis, or bleeding into the jointĮxcess weight and obesity may also increase the risk by placing strain on the knee.infections, such as Lyme disease or syphilis.overuse, due to certain physical activities or sports.a traumatic injury, leading to a fracture or ligament damage Knee joint effusion-synovitis: Knee effusion-synovitis maximal volume/area at suprapatellar pouch will be measured at screening and week 52, and severity will be scored from 0 to 3 according to the estimated maximal distension of the synovial cavity by assessing the amount of intra-articular fluid-equivalent signal on T2-weighted MRI.Tests on fluid may show that one of the following has occurred or is present:
Knee effusion how to#
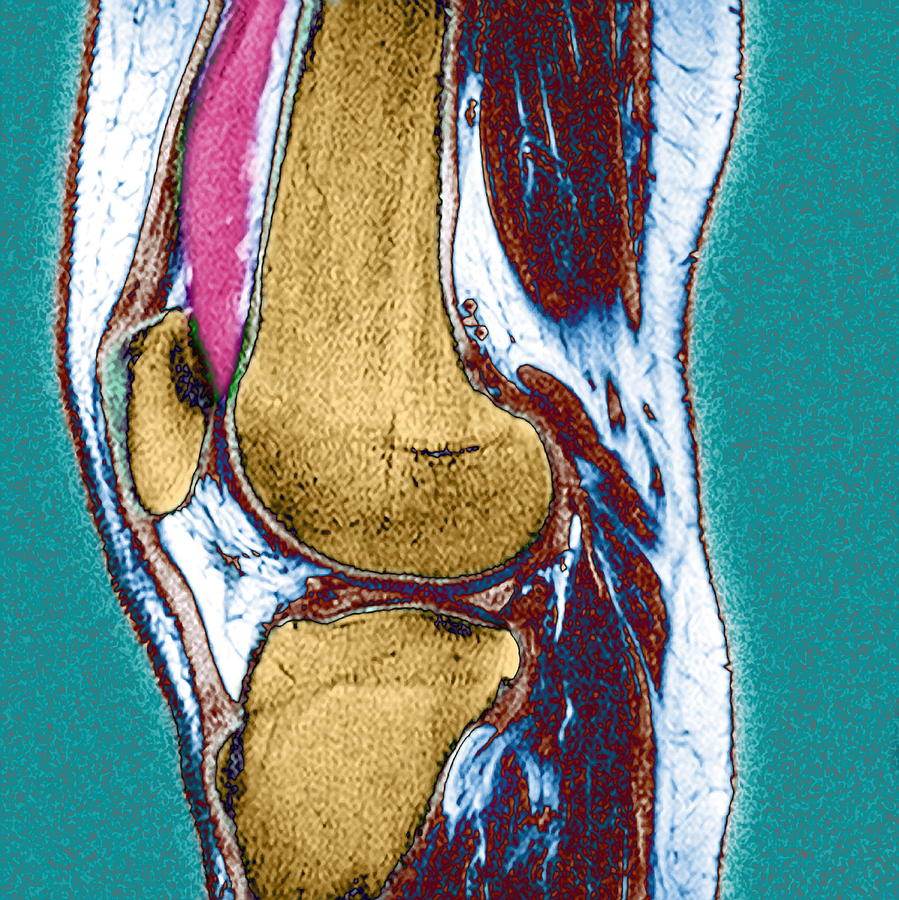
The results will show them what caused the problem and how to treat it. This is due to hemorrhage or hematoma around the patellar tendon and associated increased opacity of the retropatellar fat pad (Fig. On lateral radiograph, the effusion appears as soft tissue opacity. This can cause pain and swelling in the affected joint. An immediate post-traumatic knee effusion indicates an intra-capsular injury, such as a ligament tear, but not necessarily a fracture 6. A doctor may remove some of the fluid and send it for testing in the lab. Knee effusion is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the knee joint. The type of fluid that accumulates around the knee depends on the underlying disease, condition, or type of traumatic injury that caused the excess fluid. There are treatments you can try at home in addition to ones prescribed by your healthcare provider. Joint effusion can be a sign of an injury, a type of arthritis or another condition. Fluid on the knee can cause discomfort and is usually a sign that something is wrong. If your knee looks larger than usual, you might have joint effusion (a swollen joint).

Inflammation and swelling can result from a traumatic injury, arthritis, or an infection. 6B 13-year-old girl with juvenile idiopathic arthritis who presented with persistent knee swelling and pain. Share on Pinterest A traumatic knee effusion may feature puffiness or swelling of the joint and surrounding area. A, Sagittal ultrasound image of left knee shows joint effusion (E) in suprapatellar fossa with synovial thickening (arrows) and proliferation (asterisk).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
